
Fake Google Chrome Updates Pushed on Hacked Websites
With billions of daily users, Google Chrome is the leading internet browser in the US, with more than 63% of the market share worldwide. That’s one reason cybercrooks are targeting Google Chrome and its users with fake updates to the Chrome browser. It also brings to light the fact that telling the difference between what’s real and what’s not is getting increasingly difficult. Using fake Google Chrome updates is a way to get malware to the masses, with over 5 billion mobile installations of Chrome in 2019 alone.
What everyday users should remember is that what seems (and looks) real may not be genuine at all. Cybercriminals are focused on making that determination even more difficult, especially considering how many successful hacks start by appearing legitimate and end with abuse of user trust. WordPress users are being targeted with bogus Google Chrome updates. Bad actors are exploiting security flaws in WordPress plugins to their benefit. Instead of getting their browser updated, WordPress/Google Chrome users are downloading malware that ultimately takes control of their device from remote locations.
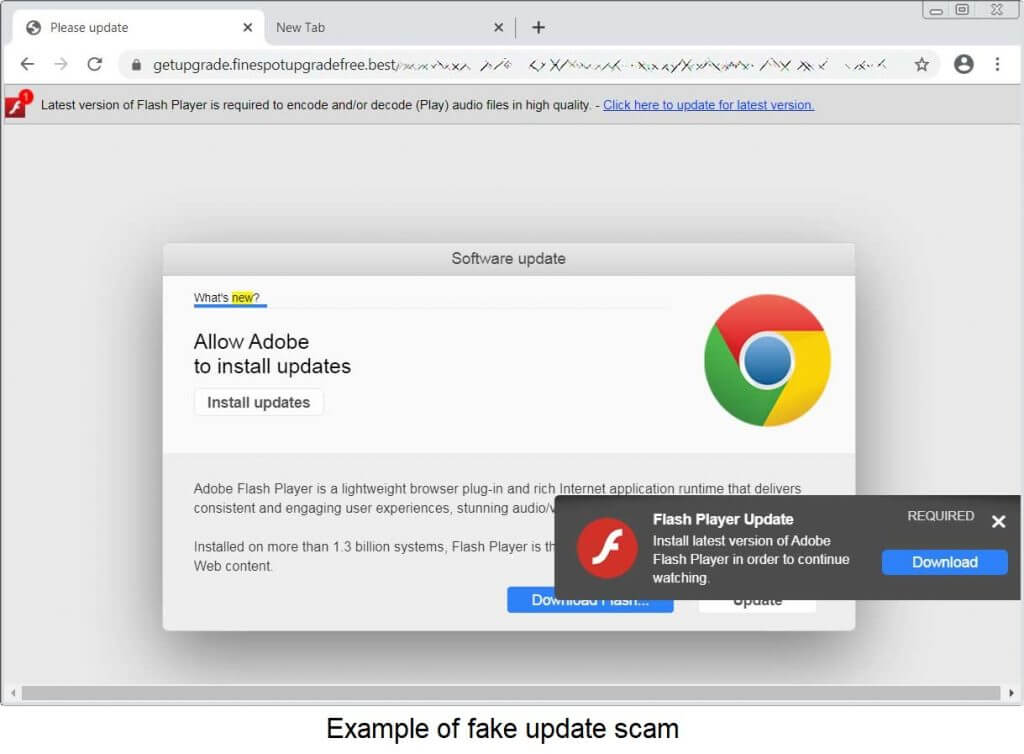
Trusting what you see online isn’t easy. For years now, we know bad actors have infiltrated social media, news, politics, healthcare, finances, and other staples of everyday life. Behind this latest scam are hackers who have pirated corporate, government, and other websites as their own. They use these fake-but-legitimate-looking websites as a launching pad for the Chrome update virus. Hacked corporate sites and news blogs running on WordPress CMS (content managing system) are being used to deliver “backdoor” malware as a means of taking over a device. Backdoor malware pretends to be something it’s not–like a fake Google Chrome update.
Backdoor malware attacks on WordPress plug-ins lets hackers insert data-stealing malware, with hundreds of thousands of websites exposed to the attacks. Among the data-hijacking downloads are other Trojans, keylogging (records every touch of a keyboard character), adware, spyware, ransomware, and a host of other malware.
With hacks like the bogus Google Chrome update being used as a weapon, “keeping it real” no longer applies as long as hackers see “keeping it fake” as much more lucrative.
By Stickley on Security

